Our Capabilities
We’re committed to providing specialist ear, nose, throat services, head and neck assessment, and surgical services. Click the below links to find out more about what we do.
- Minor
Biopsies - Hearing
Tests - Nasal
Cautery - Nasendoscopy
Services - Removal of Minor
Foreign Bodies - Ear Toilet
(Aural Toilet) - Ultrasound of
Neck & Thyroid - Tonsillectomy/
Adenoidectomy - Septoplasty
Services - Turbinate
Reduction - Functional Endo-
scopic Sinus Surgery - Myringotomy &
Grommets - Sleep Apnoea
Surgery - Thyroid/Parathyroid
/Neck Surgery
Minor Biopsies
On occasion, biopsy of tissues in the ear, nose or throat are performed under local anaesthesia in our practice rooms. Furthermore, Dr Pearson performs some neck lump and thyroid biopsies under ultrasound guidance.
Prof MacKay and Dr Pearson will advise whether your biopsy is appropriate for the rooms or whether it should be arranged in the operating theatre. Most biopsy results take around one working week to come back.
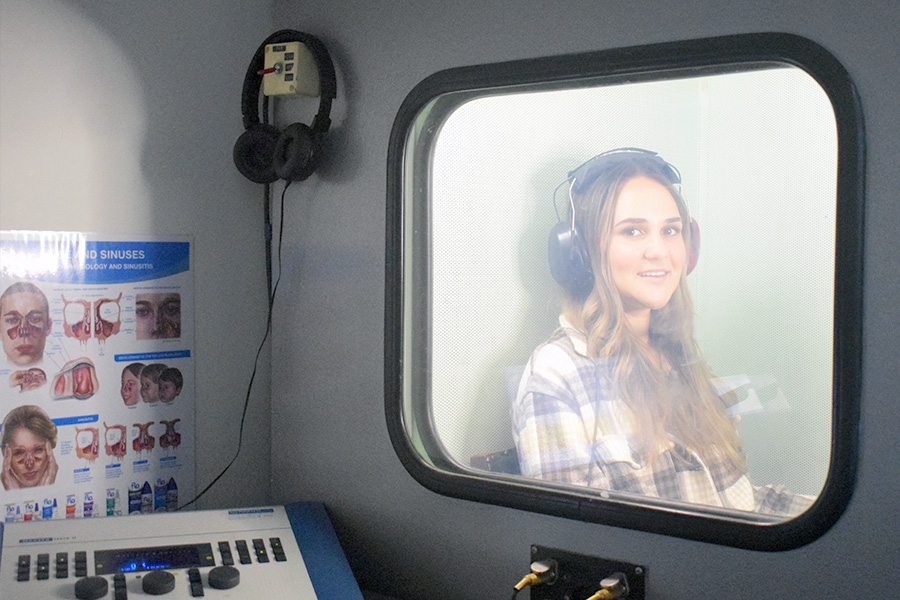

Hearing Tests
Illawarra ENT Head & Neck Clinic offers formal hearing tests with audiogram, tympanogram, speech reception testing etc for all patients six years and over. Occasionally some five year olds and even four year olds are suitable for these hearing tests.
The majority of ear conditions require some form of hearing assessment. Children with grommets and adults with chronic conditions often require repeated tests, as do all patients who have undergone ear surgery.
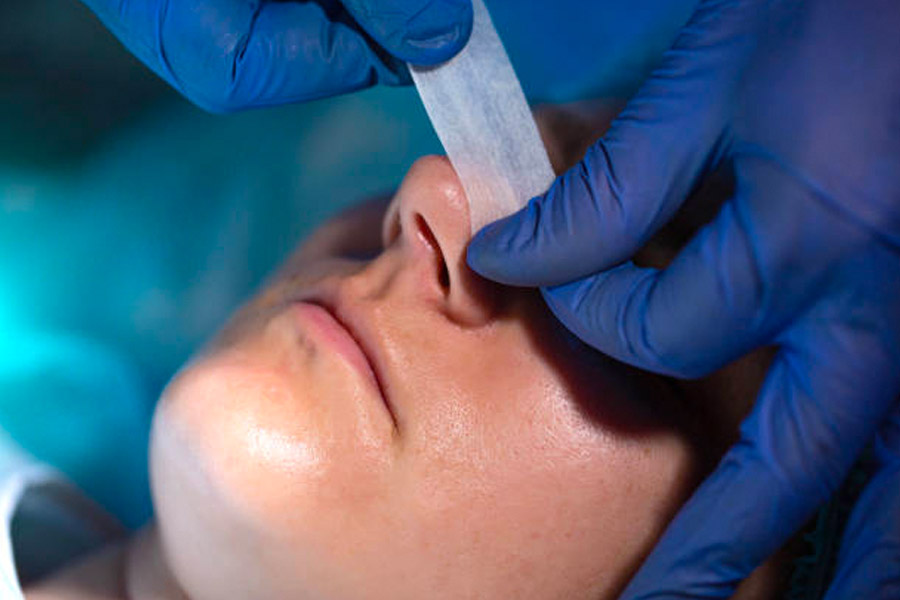
Nasal Cautery
Cautery for epistaxis (“nose bleeds”) is performed in the rooms with topical anaesthesia in the majority of cases.
On some occasions, the operating theatre is utilised. Often topical cream or ointment is applied to the cauterised area for 1-2 weeks and follow up is arranged.
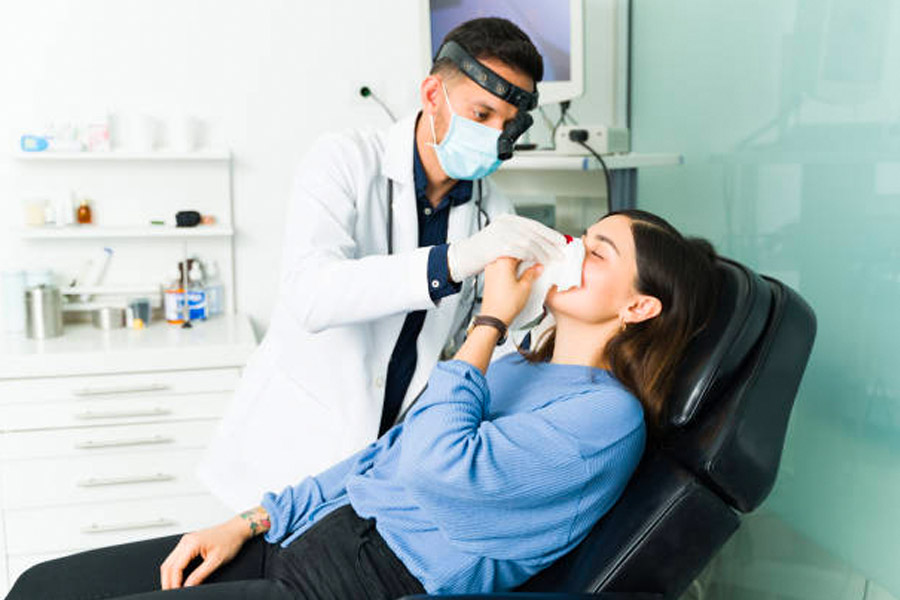
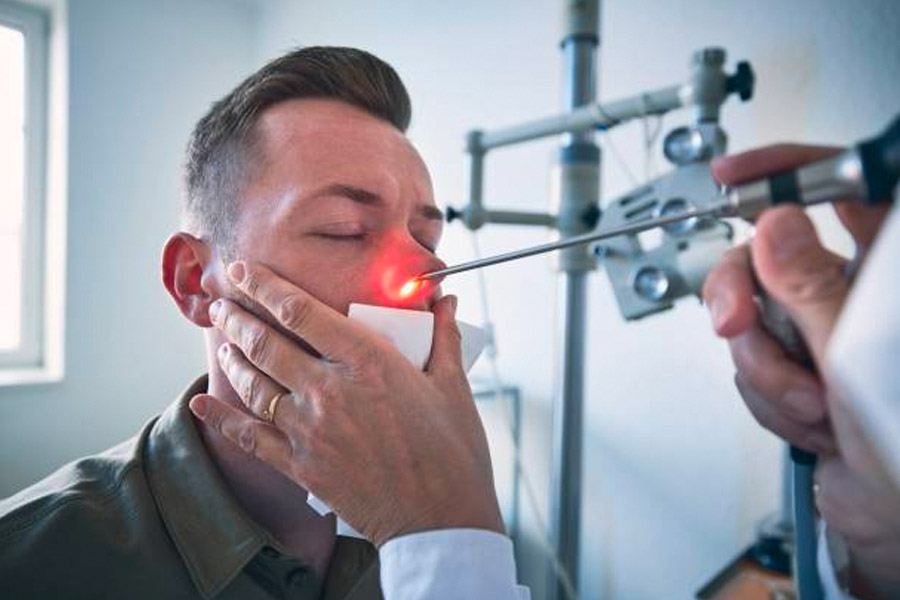
Nasendoscopy
Office Nasendoscopy involves topical (“spray”) anaesthesia and passage of a rigid or flexible tube into the nose to assess the nasal +/- upper airway. The procedure is brief and generally painless, with patients able to return to work/school immediately after examination completed. Many conditions require this assessment including but not exclusively:
- Recurrent nose bleeds
- Nasal and sinus problems
- Globus/reflux
- Voice/swallowing problems
- Pre and post thyroid surgery
- Adenoid assessment
- Snoring assessment
Technique Utilised:
- Preparation of the nasal cavity and throat with local anaesthetic spray
- Single use sterile sheath placed over scope for hygiene
- Connection of scope to processor and monitor
- Image capture program opened in electronic patient file
- Passage of scope in nasal cavity and upper throat
- Patient can view live images during consultation
- Photos taken if point of interest identified
- Scope removed and sheath discarded
- Local anaesthetic wears off in 20min – able to eat/drink
- Well tolerated in children and adults
- Local anaesthetic prevents gag and vomit reflexes
- Able to return to work/school immediately after procedure

Removal of Minor Foreign Bodies
Minor ear, nose and throat foreign bodies can be removed in our rooms using microscopic or nasendoscope equipment. Sometimes general anaesthesia in the operating theatre is required. Foreign bodies often need urgent attention, especially if related to acid or alkaline ingestion (e.g. battery) or active/alive foreign bodies (e.g. insects).
Ear Toilet (Aural Toilet)
Technique of cleaning the external ear canal under the microscope. Performed with patient seated comfortably or reclined, this is used to manage a variety of ear canal disorders including:
- Wax impaction
- Otitis externa – external canal infection
- Middle ear infection with perforation of ear drum
- Foreign body
- Furunculosis – abscess in ear canal
- Cholesteatoma of ear canal
- Clear skin/wax debris to assess ear drum and middle ear
Techniques Utilised:
- Wax curette – blunt ring instrument to remove dry debris
- Suction – microscopic suction tip
Ultrasound of Neck & Thyroid
Ultrasounds are a medical imaging technique using high frequency sound waves.
Our ultrasounds are radiation free and safe for use on all individuals. Helpful for providing a detailed assessment of the thyroid gland, neck and saliva glands, this may be used to guide a fine needle in obtaining a tissue biopsy.
Technique Utilised:
- Position patient reclined on clinic chair
- Details are entered in the ultrasound registration form
- Neck is exposed and paper apron placed to protect clothing from gel
- Ultrasound gel is applied to the site to be studied and the ultrasound probe
- Probe placed with light pressure on neck, images taken
- Fine needle used if biopsy taken – band aid applied
- Gel removed from neck
- Probe sterilised before storage
- Patient able to return to work after procedure
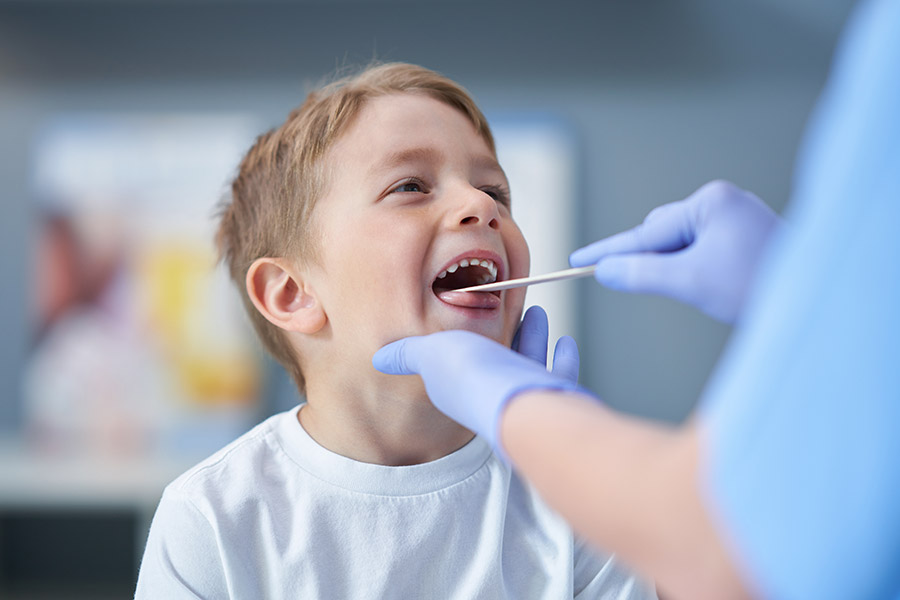
Tonsillectomy / Adenoidectomy
Surgical removal of the palatine (“tonsillectomy”) or nasopharyngeal tonsil (“adenoidectomy”) is often performed concurrently (“adenotonsillectomy”). General anaesthesia is necessary. Most tonsillectomy and adenotonsillectomy involves an overnight stay in hospital, whereas adenoidectomy is often performed as a day procedure, depending upon age.
Perioperative care is extensively planned and Prof MacKay and Dr Pearson will discuss this with you during consultation. Examples of the post operative information sheets and potential risks of surgery are included below.
Septoplasty
“Septoplasty” refers to correction of bends or spurs in the bony end or cartilaginous nasal septum, which separates the right from left nostril. It is often performed concurrently with other nasal surgery (e.g. turbinoplasty, sinus surgery, etc), and may be as a day stay or overnight procedure.
The operation is usually to improve nasal obstruction, or facilitate sinus surgery, or as a “prephase” to improve the nasal airway in adult obstructive sleep apnoea.
Turbinate Reduction
Turbinate reduction is usually concurrent with septoplasty, but not always, and involves reduction of the inferior turbinates (“meat of the nose”).
Generally nasal obstruction is the reason for this intervention.
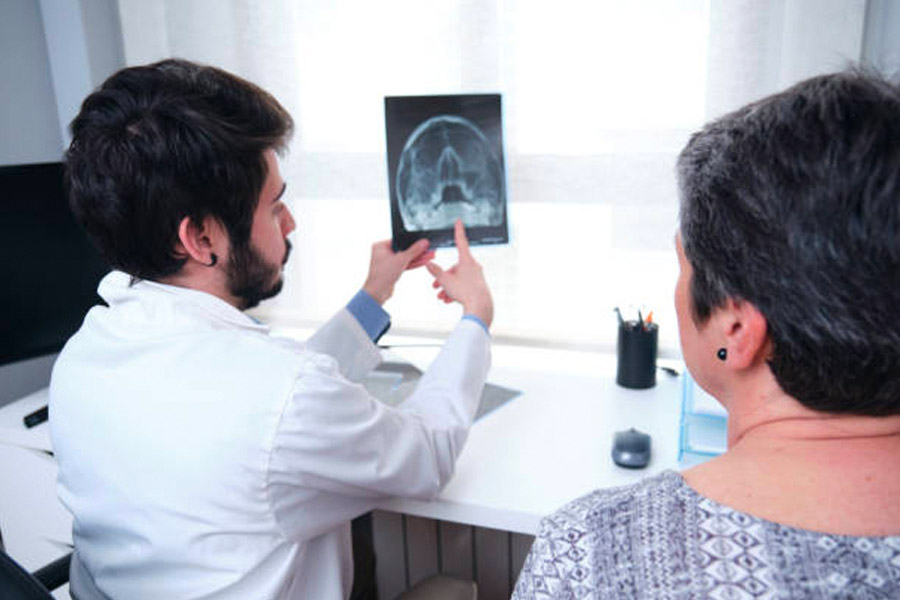
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
Surgery performed via the inside of the nose to open sinuses is called “FESS”. It may be concurrent with septoplasty and turbinate reduction. Dr Pearson and Prof MacKay will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of such surgery with you, but it is often performed for failed medical therapy or symptoms persistent despite other treatments.
Myringotomy & Grommets
“Myringotomy” involves incision of the tympanic membrane (“eardrum”), usually to drain middle ear fluid. “Grommet insertion” is usually performed at this time. A Grommet is a Pressure Equalization Tube (Ventilation Tube), that allows equalization of pressure between the middle ear and external ear/environment, in order to prevent fluid build up and consequent hearing loss. There are many indications, especially in children, including hearing loss, glue ear, recurrent ear infections, complicated ear infection, etc. Adenoidectomy or assessment of the adenoids with nasendoscopy is often performed at the same time.

Sleep Apnoea Surgery
Prof MacKay is internationally renowned for this surgery. He completed a fellowship under his mentor, the late Dr Sam Robinson.
Thyroid/Parathyroid/Neck Surgery
Our thyroid/parathyroid/neck surgeries are performed with preoperative nuclear scans and ultrasound. By performing intraoperative blood tests, we improve the success rates for surgery.